ANOTHER year, and another announcement from the Australian Bureau of Meteorology that it is getting hotter. Indeed on January 3, 2014, David Jones, Manager of Climate Monitoring and Predictions at the Bureau, explained in a radio interview that: “We know every place across Australia is getting hotter, and very similarly almost every place on this planet. So, you know, we know it is getting hotter and we know it will continue to get hotter. It’s a reality, and something we will be living with for the rest of this century.”
I’m not sure that its going to continue to get hotter, but last year was hot.
According to Dr Jones, the hottest place in 2013 was Moomba in South Australia where a temperature of 49.6°C was recorded in January. What Dr Jones didn’t explain, however, is that temperatures have only been recorded at Moomba since 1995. So we don’t actually know how hot it was at Moomba during the federation drought or in 1939.
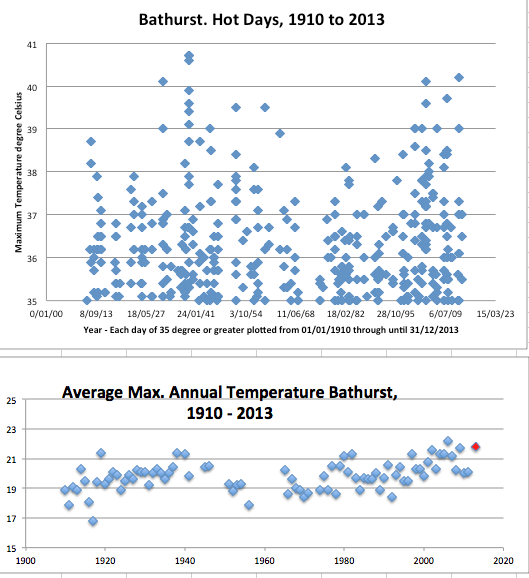
I’ve been following trends at Bathurst where temperatures have been recorded at the jail since 1858 and at the agricultural college since 1908. In October, after plotting days when maximum temperatures exceeded 35 degree Celsius, I indicated that there has been no increase in hot days at Bathurst, http://www.mythandthemurray.org/no-increase-in-hot-days-at-bathurst-or-the-misguided-politics-of-attributing-bushfires-to-global-warming/ .
But after plotting the really hot days through until the end of 2013, I’m happy to concede that it’s virtually as hot now as it was back in 1939, Chart 1. On 11th January 1939 temperatures climbed to 40.7 degrees at the Bathurst agricultural station. In January last year it reached 40.2 degrees. Furthermore, when averages maximum temperatures are combined for each year, there appears to be a slight warming trend, Chart 2.
Unfortunately, the average for the year 1939 is not shown in Chart 2 as maximum daily temperatures are not available in the digitized record for May through to September of that year for this site. The hottest year at the Bathurst agricultural college according to this statistic (whereby maximum daily temperatures are averaged for the year) was 2006 with an annual average maximum daily temperature of 22.2 degrees compared to an average maximum for 2013 of 21.8 degrees.
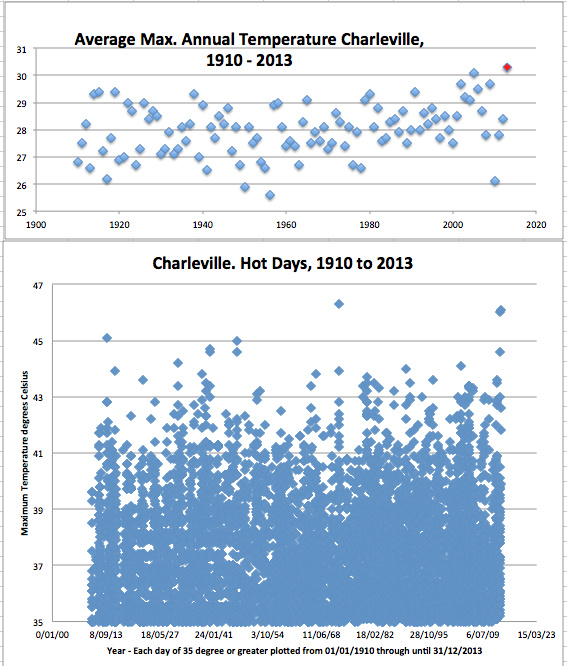
If we go further north to western Queensland and consider the long temperature trend for Charleville, then last year appears to be a record hot year, Chart 3. All years are shown from 1910 based on my averaging of the available daily maximum values from the Bureau’s homogenized ACORN* data set to the end of 2012. I’ve relied on the raw daily values for 2013. I’ve made no adjustments for missing values in this record and have not compared the raw data to the end of 2012 with the ACORN-SAT adjusted data.*
When individual hot days are plotted for Charleville, the hottest day at 46.3 degree Celsius shows as 4th January 1973, Chart 4. This is closely followed by 46.0 degrees recorded just last year on 29th December 2013. And just a few days ago, on 3rd January 2014, it was 46.1 degrees at Charleville.
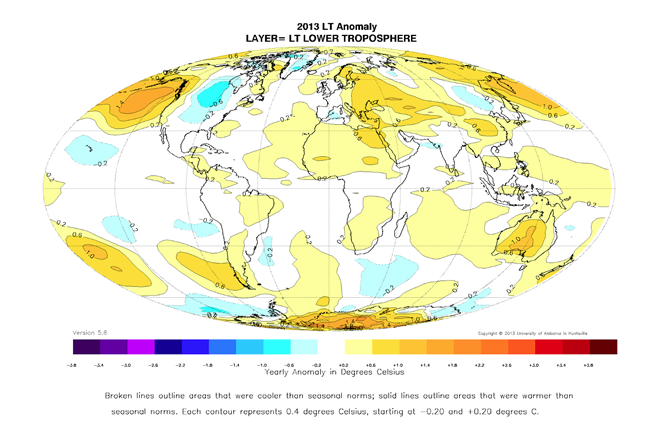
The hotter than average conditions in Australia for 2013 show up in the satellite record as published by the University of Alabama in Huntsville, Chart 5. According to this record, globally 2013 was the fourth warmest year since measurements began in 1978, http://wattsupwiththat.com/2014/01/03/global-temperature-report-december-2013/ .
*****
ACORN-SAT is the Australian Climate Observations Reference Network – Surface Air Temperature. Data can be downloaded here http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/change/acorn-sat/ .
Ken Stewart, John Sayers, Jo Nova and others have shown up many issues with this database, for example, http://joannenova.com.au/2012/06/threat-of-anao-audit-means-australias-bom-throws-out-temperature-set-starts-again-gets-same-results/ . It nevertheless remains a useful source of information. For the Bathurst agricultural station the long unadjusted data set (recently purchased by me from the Bureau) accords well with the publically available ACORN dataset. I have no particular opinion on the reliability of the Charleville ACORN data as I do not have access to the unadjusted Charleville data before 1948.









 Jennifer Marohasy BSc PhD has worked in industry and government. She is currently researching a novel technique for long-range weather forecasting funded by the B. Macfie Family Foundation.
Jennifer Marohasy BSc PhD has worked in industry and government. She is currently researching a novel technique for long-range weather forecasting funded by the B. Macfie Family Foundation.