THE Australian Bureau of Meteorology, BOM, doesn’t have a set of temperature thermometers regularly positioned across the landmass of Australia from which it might derive an average annual temperature. Rather many more of it’s approximately 750 temperature recording stations are in south eastern Australia, some have records that date back to the 1850s, while others only started recording last year.
How do you derive an average annual temperature for Australia from such a mix of measurements? 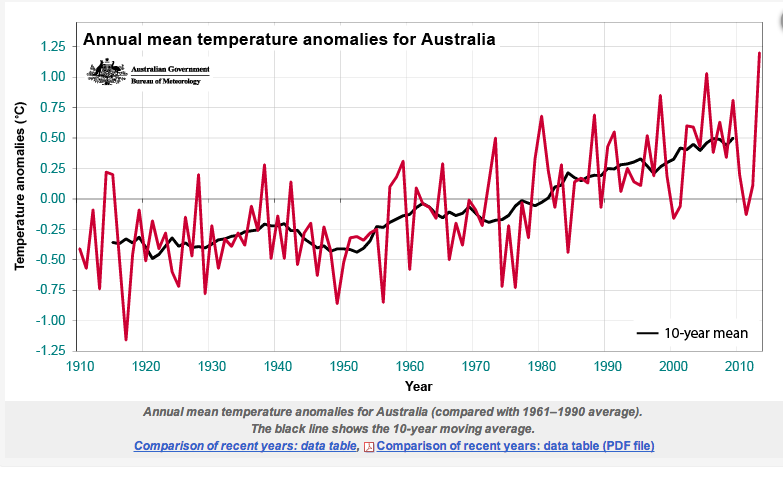
The Bureau’s solution is to select a subset of about 112 stations from the 750. Some of the stations in the subset started recording temperatures in the 1850s, others not until the 1960s. Then the bureau truncates the longer temperature records, in some cases by discarding over 50 years of data, indeed everything before the somewhat arbitrary date of 1910. Data before this date is not considered reliable, but then the Bureau applies corrections to some of the rest of the data even though it should be reliable. Then the adjusted and truncated values from the subset are fitted to a grid to generate an area-weighted average of the data.
There is no single document that describes this methodology. Rather in a letter from the Bureau dated 24th January, responding to my request for information, I was directed to a mix of Bureau reports, peer-reviewed papers and also a PhD thesis by way of justification, methodology and for a list of stations.
In short, there is no straightforward way to verify the claim that last year, 2013, was the hottest calendar year on record. This is the claim the Bureau made in a media release on 3rd January 2014.
When individual stations with long temperature records are examined the late 1890 and 1930s appear to be as hot as recent years.
Ever since Climategate, deeply disturbing questions have been asked about the way climate science is conducted and also the state of the climate data. The Australian Bureau of Meteorology’s own databases feature in the leaked emails with the infamous ‘Harry Read Me’ file complaining about jumbled values and incorrect start dates for particular stations.
The mainstream climate science community has a vested interest in the average temperature for Australia increasing year-on-year because it has embraced the theory of anthropogenic global warming and invested heavily in research that assumes this theory.
It is time that the Bureau was more transparent in how it calculated its average annual values, and that it developed a method for benchmarking these annual average values. The benchmarking could be against satellite data and also against individual stations in Australia for which there are long temperature records.
**************
Click here to download the Bureau’s reply to my letter of 9th January requesting information to enable verification of the claim that 2013 was the hottest year on record.
Click on the image to see a chart of the Bureau’s annual mean temperature anomaly for Australia, this value is derived from the annual mean.

 Jennifer Marohasy BSc PhD has worked in industry and government. She is currently researching a novel technique for long-range weather forecasting funded by the B. Macfie Family Foundation.
Jennifer Marohasy BSc PhD has worked in industry and government. She is currently researching a novel technique for long-range weather forecasting funded by the B. Macfie Family Foundation.